22+ US Literacy Statistics: Literacy Rate, Average Reading Level


Looking For The Latest and Greatest Literacy Statistics?
Only 57% of adults in the United States have proficient literacy skills, and nearly 32 million adults are functionally illiterate.
This means that they cannot read above a basic level or complete tasks such as filling out a job application or interpreting a simple set of instructions. Even more alarming is that these numbers have not improved in decades.
Top U.S. Literacy Rate Statistics
- 14% of U.S. adults can’t read.
- 21% of adults read below a 5th-grade level.
- 19% of high school graduates can’t read.
- 43% of adults with low literacy live in poverty.
- 50% of adults with low literacy do not have a job.
- 85% of juvenile offenders have low literacy skills.
- 3/4 of state prison inmates did not graduate high school.
- 2/3 of students who cannot read proficiently by the end of the 4th grade will end up in jail or on welfare.
- 1 in 4 children in America grows up without learning how to read.
- 32 million adults in the U.S. can’t read.
- 14% of U.S. adults are considered “functionally illiterate.”
- 21% of adults in the U.S. read below a 5th-grade level.
- 19% of high school graduates in the U.S. can’t read.
- 42 million U.S. adults can’t read past a 5th-grade level.
- 50% of adults in the U.S. can’t read a book written at an 8th-grade level.
- 33% of 4th graders in the U.S. cannot read at a basic level.
- 20% of U.S. high school seniors can’t read.
- 2/3 of students who cannot read proficiently by the end of the 4th grade will end up in jail or on welfare
- 75% of state prison inmates did not graduate high school.
- 1 in 6 children who are not reading proficiently in 3rd grade will not graduate from high school on time, a rate 4 times greater than that for proficient readers.
- Only 1 in 3 children who enter kindergarten with below-average literacy skills will read proficiently by third grade.
- 1 in 3 low-income children doesn’t have any books at home.
Additional Facts on U.S. Literacy Statistics
- 46% of American adults cannot understand basic financial documents like balance sheets and income statements.
- 75% of Americans who receive food stamps perform at the lowest two levels of literacy.
- 90% of U.S. employers have difficulty filling positions due to a lack of qualified candidates with the necessary skills, including literacy.
- 77 million Americans lack basic literacy skills required for most jobs in the U.S.
- The National Assessment of Educational Progress found that only about 37% of high school seniors were proficient or advanced in reading in 2021.
General U.S. Literacy Statistics
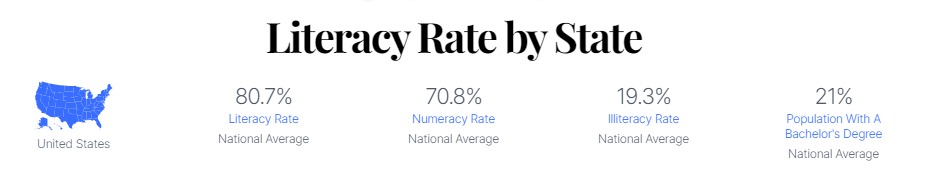
- According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), 79% of American adults have medium to high English literacy skills.
- This means that 21%, or about 43 million adults, have low literacy skills, bordering on illiteracy.
- Low levels of literacy can negatively affect the U.S. economy due to loss of employment opportunities and workforce productivity. It has been estimated that low levels of literacy cost the U.S. $2.2 trillion per year.
- Low levels of literacy may also lead to political disengagement, greater dependency on social welfare programs, and higher crime rates.
- Compared to other developed nations, the U.S. has lower literacy rates.
- Immigration is an important factor contributing to illiteracy in the U.S., with 34% of those who lack English literacy proficiency being born outside the country.
- States with large communities of immigrants born outside the United States tend to have lower adult literacy rates.
- Children's literacy rates are also important, as low literacy rates in childhood can cause similar damaging effects on a nation's overall health.
- In 2013, 66% of 4th graders across the U.S. were reading below proficiency levels.
- Low childhood literacy levels may lead to prolonged low adult literacy rates, which will negatively impact the nation's well-being.
Most Literate States in U.S. (2023)
- New Hampshire has the highest literacy rate in the US, with a rate of 88.5%.
- This means that nearly 90% of the population over age 25 can read and write at least at a basic level.
- The high rate of literacy is attributed to several factors, including well-funded public schools, access to higher quality education, consistently high scores on national standardized tests for mathematics and reading comprehension, low poverty rate, which contributes significantly to high literacy rates
- New Hampshire has seen steady improvements in its overall literacy rate over time, despite changes in population.
- This suggests that both public policy initiatives and grassroots efforts have been successful in improving educational outcomes across all demographics.
U.S. States with the Lowest Literacy Rates (2023)
- According to recent data, New Mexico has the lowest literacy rate among US states, with only 70.9% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills.
- California has the second lowest literacy rate in the US, with 71.6% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills.
- Texas and Mississippi have the third and fourth lowest literacy rates among US states, with only 71.8% of their adult populations having basic or below basic literacy skills.
- Louisiana has the fifth lowest literacy rate among US states, with only 72% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills. Nevada has the sixth lowest literacy rate, with 74.7% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills.
- New York has the seventh lowest literacy rate in the US, with 75.6% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills. At 76.1%, Alabama is the eighth state with the lowest literacy rate.
- Florida has the ninth lowest literacy rate among US states, with only 76.3% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills.
- Georgia rounds out the list of states with the lowest literacy rates, with a rate of 76.4% of its adult population having basic or below basic literacy skills.
Child Literacy in the U.S.: Key Statistics
- Only 36% of fourth-grade students in the United States are proficient in reading (National Assessment of Educational Progress, 2019).
- Children who are not reading at grade level by third grade are four times more likely to drop out of high school than proficient readers (Annie E. Casey Foundation, 2010).
- Approximately two-thirds of students who cannot read proficiently by the end of fourth grade will end up in jail or on welfare (National Institute for Literacy).
- Children from low-income families often face additional barriers to literacy, and only one in three low-income children has access to books at home (Reading Is Fundamental).
- According to the National Assessment of Educational Progress, 80% of low-income fourth-graders are not reading at grade level.
How Many Children Can't Read?
- According to the National Assessment of Educational Progress, only 36% of fourth-grade students in the United States are proficient in reading.
- Children who are not reading at grade level by third grade are four times more likely to drop out of high school than proficient readers, as reported by the Annie E. Casey Foundation.
- The National Institute for Literacy states that approximately two-thirds of students who cannot read proficiently by the end of fourth grade will end up in jail or on welfare.
- Reading Is Fundamental reports that children from low-income families often face additional barriers to literacy, and only one in three low-income children has access to books at home.
- The National Assessment of Educational Progress found that 80% of low-income fourth-graders are not reading at grade level.
Measuring Student Proficiency
- According to the National Assessment of Educational Progress, only 36% of fourth-grade students in the United States are proficient in reading.
- In 2021, the National Assessment of Educational Progress found that only about 37% of high school seniors were proficient or advanced in reading.
- The Annie E. Casey Foundation reports that children who are not reading at grade level by third grade are four times more likely to drop out of high school than proficient readers.
- The National Institute for Literacy states that approximately two-thirds of students who cannot read proficiently by the end of fourth grade will end up in jail or on welfare.
- Reading Is Fundamental reports that children from low-income families often face additional barriers to literacy, and only one in three low-income children has access to books at home.
Child Literacy Rates by State: A State-by-State Comparison
Here are some statistics on Child Literacy Rates by State (4th grade) in the United States:
- Massachusetts has the highest percentage of fourth-grade students who scored at or above proficient in reading, with 53%.
- Mississippi has the lowest percentage of fourth-grade students who scored at or above proficient in reading, with only 20%.
- Other states with low percentages include New Mexico (22%), Louisiana (23%), and Alabama (24%).
- On average, about 35% of fourth-graders across all states scored at or above proficient in reading.
Factors Contributing to Child Illiteracy
- Children from low-income families are more likely to experience food insecurity, which can negatively impact their cognitive development and lead to lower literacy rates. In fact, children who experience food insecurity are twice as likely to have below-average reading skills compared to their peers who do not experience food insecurity (Feeding America).
- Dyslexia is a common learning disability that affects reading and writing skills. It is estimated that 1 in 5 students has dyslexia, yet only 1 in 50 teachers receives training in dyslexia intervention (Dyslexia Center of Utah).
- Limited access to early childhood education can also contribute to child illiteracy. In the U.S., only about half of all three- and four-year-olds are enrolled in preschool programs (National Institute for Early Education Research).
- Children who come from homes where English is not the primary language spoken may also be at a disadvantage when it comes to literacy. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, English Language Learners (ELLs) have lower average reading scores than non-ELLs.
Adult Literacy Statistics
- Only 57% of adults in the United States have proficient literacy skills (National Center for Education Statistics).
- Nearly 32 million adults in the U.S. are functionally illiterate, meaning they cannot read above a basic level or complete tasks such as filling out a job application or interpreting a simple set of instructions (ProLiteracy).
- 46% of American adults cannot understand basic financial documents like balance sheets and income statements (National Adult Literacy Survey).
- 75% of Americans who receive food stamps perform at the lowest two levels of literacy (National Assessment of Adult Literacy).
- 77 million Americans lack basic literacy skills required for most jobs in the U.S. (ProLiteracy).
How Many Adults Can't Read?
- According to ProLiteracy, nearly 32 million adults in the U.S. are functionally illiterate, meaning they cannot read above a basic level or complete tasks such as filling out a job application or interpreting a simple set of instructions.
- National Center for Education Statistics reports that only 57% of adults in the United States have proficient literacy skills.
- The National Assessment of Adult Literacy found that 75% of Americans who receive food stamps perform at the lowest two levels of literacy.
- ProLiteracy also states that 77 million Americans lack basic literacy skills required for most jobs in the U.S.
Adult Literacy Rates by State in the United States
- Vermont has the highest percentage of adults with proficient literacy skills, with 68%.
- California has the lowest percentage of adults with proficient literacy skills, with only 43%.
- Other states with low percentages include Louisiana (48%), Mississippi (49%), and Arkansas (50%).
- On average, about 57% of adults across all states have proficient literacy skills.
Closing Thoughts
In conclusion, literacy rates have a significant impact on the well-being of individuals and society as a whole. Low literacy rates are linked to higher poverty rates, lower educational attainment, and even increased likelihood of incarceration.
It is important for policymakers to prioritize funding for education initiatives that promote literacy and for communities to take action in providing access to books and educational resources. Additionally, early childhood education programs and dyslexia interventions can help prevent low literacy rates from persisting into adulthood.
Sources
- National Assessment of Educational Progress. (2019). The Nation's Report Card: Reading Highlights 2019.
- Annie E. Casey Foundation. (2010). Early Warning! Why Reading by the End of Third Grade Matters.
- National Institute for Literacy. (2008). Adult Literacy Facts.
- Feeding America. (2016). Map the Meal Gap: Child Food Insecurity.
- Dyslexia Center of Utah. Dyslexia Facts and Statistics.
- National Institute for Early Education Research. (2020). The State of Preschool Yearbook 2020.
- National Center for Education Statistics. (2021). The Nation's Report Card: Reading 2019 - Minnesota.









